The Hybrid Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM) is used to simulate the Java Sea mean sea
level, surface current and volume transport. The model (JSD, Java Sea Domain) is driven
by the European Remote Sensing (ERS) satellite-derived and National Center
Environmental Prediction (NCEP) wind stresses. The ERS-derived and NCEP wind
speeds and stresses are compared to investigate the impacts of the different wind
forcing data on the estimation of the Java mean sea level. The validation results illustrate
that the simulated mean sea levels agree well with the tide gauge sea levels. The
NCEP wind-driven JSD (called NJSD) model has correlation coefficients from 0.53 to 0.84
and root mean square errors (RMSE) of 47 mm to 76 mm. On the other hand, the ERS
wind-driven JSD (Called EJSD) model has the correlation coefficients from 0.71 to 0.89
and RMSEs of 40 mm to 61 mm against tide gauge sea level, respectively. These
validation results reveal that accuracy of the EJSD model is better than the NJSD
model.
The relationship between the Java Sea zonal wind and volume transport is also
investigated by using HYCOM. Due to the shallowness of the Java Sea, the volume
transport is dominated by the wind, which is greatly different between ERS and NCEP.
The Java Sea volume transport is directed eastward and westward during the
northwest (October to March) and southeast (April to September) monsoons,
respectively. The westerly and easterly ERS wind stresses in December and August are
0.01 N/m
2
and 0.03 N/m
2
higher than NCEP wind stresses, respectively. Moreover, the
NCEP mean wind speed is 1.0 m/s and 2.5 m/s lower than ERS mean wind speed, during
the northwest and southeast monsoons, respectively. Consequently, the Java Sea
eastward volume transport simulated by the EJSD model is found to be larger than the
one simulated by the NJSD model. The EJSD model-simulated Java Sea eastward and
westward volume transports in December and August are 0.23 Sv and 0.30 Sv larger than
the ones simulated by the NJDS model, respectively.
Key words: Java Sea, ERS wind, NCEP wind, HYCOM. INTRODUCTION
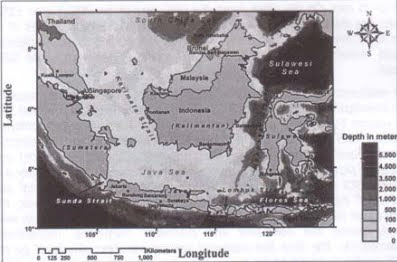
The location of the Java Sea and the Makassar Strait is depicted in Figure 1. The
Java Sea has average depths from 40 m to 50 m. The Java Sea is bordered by the
Kalimantan Island to the north, the Java Island on the south, the Sumatra Island on the
west, the southern Makassar Strait on the east, the Karimata Strait on the northwest, and
the Sunda Straits on the southwest.
Many studies on the Indonesian troughflow (ITF) have been conducted through the
Arlindo (Arus Lintas Indonesia, [1,2,3]) project and others. Unfortunately, most of the
scientists neglected what was happening in the Java Sea due to its shallowness [4]. The
past observation [5] and NCEP wind-driven ocean model results [6,7] show that the Java
Sea low-salinity surface water shifts into the southern Makassar Strait during the
northwest monsoon from October to March. The southeast monsoon winds return the lowsalinity water back into the Java Sea during the southeast monsoon from April to
September. Sofian et al. [6] also argue that the strong westward volume transport
generates high sea level within the Java Sea. Moreover, the Java Sea transport is directed
eastward during the northwest monsoon, from October to March, and to the westward
during the southeast monsoon from April to September, following the monsoonal wind-indivvidu
Figure 1: Bathymetric map of the Indonesian Sea, including the Sunda, and
Karimata Straits, the South China Sea, the Java Sea, the Makassar Strait, the
Flores Sea, and the Sulawesi sea.
The aim of this study is to investigate the impacts of different wind forcing data on
the simulation accuracy of the Java Sea. The models are forced by the ERS and NCEP
winds. The ERS wind has a limitation on the period of data, which is only available from
1992 to 2001, while the NCEP wind is available from January 1948 to the present.
However, the NCEP wind has the limitation on the spatial resolution of 1.875° longitude
yxJ latitude, while the ERS wind has the spatial resolution of 1° longitude and latitude. '-e
present study addresses the following questions: 1) how good is the modelled mean sea
level against the tide gauge mean sea level?, 2) are the modelled mean sea levels eiable
to express the El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) impacts on the mean sea evel?, and
3) can the different wind forcing change the Java Sea volume transport?
This paper is organized as follows. The brief explanation of data used in this earch and
the model configuration are given in the section of Ocean Model. The Description of tide
gauge mean sea level data and results of model validation are described in the section of
Model Validation. The wind patterns and the climatology over the Java Sea are described
in the section of Wind Climatology. The relationship between wind and -xxJelled surface
current during the northwest and southeast monsoons are discussed in ne section of
Wind and Surface Currents. The climatology of the Java Sea volume transport is
described in the section of Java Sea Volume Transport. The final section is -stained to
concluding remarks. Ocean Model
HYbrid Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM) [8] is applied to simulate the Java Sea
and the Makassar Strait. The model region is the Indonesian Sea including the Southern
South China Sea, the Java Sea, the Sulawesi Sea, the Karimata Strait, and the Makassar
Strait, as shown in Figure 1. The horizontal grids span from 80°E to 125°E and from 10°S
to 8°N. This domain is referred to as the Java Sea Domain (JSD) hereafter, and the grid
resolution is Mercator 0.1° longitude and latitude. The model is configured with 22
layers,and the bottom topography is based on ETOP02 data. This model uses KPP (KProfileParameterization) vertical mixing, and the explanation of the method can be found
in [9]. More detail description of the HYCOM equations and numerical algorithms can be
found in [8]. The model relaxes at the lateral boundaries to the World Ocean Atlas (WOA)
1998 monthly climatology, which contains salinity and temperature profiles. Tidal forcing is
not available in HYCOM. The model is driven by weekly ERS and NCEP wind speed and
stress data. The ERS wind data are derived from Centre ERS d'Archivage et de
Traitement -Institut francais de recherche pour I'exploitation de la mer (CERSATIFREMER [10]). The ERS wind has the spatial resolution of 1° longitude and latitude. The
atmospheric forcing that contains surface air temperature, surface specific humidity, net
shortwave and longwave radiations, and precipitation are based on the NCEP reanalysis
data. The weekly NCEP data are calculated from the daily mean data. The NCEP data
have the spatial resolution of the Gaussian grid 1.875° longitude and latitude. The model's
sea surface temperature (SST) is the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
(NOAA) optimal interpolation (01) SST. The NJSD and EJSD model are nested to the
large domain model, which covers the area from 30°E to 60°W and from 45°S to 45°N.
This region is referred to as the Indo-Pacific Ocean Domain (IPD). The ERS and NCEP
wind-driven IPD models a
r
e called EIPD and NIPD models, respectively. NIPD and EIPD
models have 1° longitude nd latitude grid spacing. Moreover, the EIPD and NIPD models
use the same topography iata and parameters of the forcing fields, initial conditions, and
mixing layer model as used in the EJSD and NJSD models, respectively.
The sensible and latent heat fluxes are calculated during model runs, using the
model SST and the bulk formulae. The NJSD and EJSD models are relaxed to the NIPD
and EIPD models, respectively. The relaxation time scale increases from 0.1 to 3 days
with distance away from the boundaries. The precipitation and evaporation are also
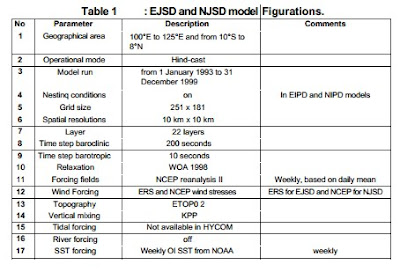
included in this model. The summary of model configurations is presented in Table 1.
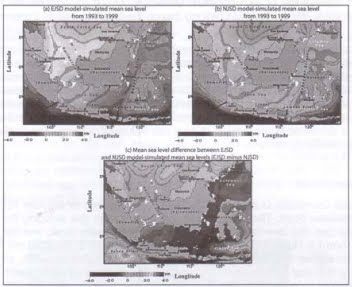
Figures 2 (a) and (b) show the EJSD and NJSD model-simulated mean sea levels for
7 years from 1993 to 1999. Figure 2 (c) shows the difference between the EJSD and NJSD
model-simulated mean sea levels. The EJSD and NJSD model-simulated mean sea levels
show similar patterns within the Indonesian Sea. The mean sea level is high at the South
China Sea and the Karimata Strait and low at the Java Sea and southern Makassar Strait.
"Tie lowest sea level is occurred at south off Java and Sumatera Islands as shown in
Rgures 2 (a) and (b). The Figure 2 (c) shows the EJSD model-simulated sea level is about
7
:m lower than the one simulated by NJSD model in the Java Sea, and reaches to 7 cm
tower at the southern Makassar Strait. Moreover, the EJSD-simulated mean sea level is 5
cm lower than NJSD-simulated sea level in the Sulawesi Sea. On the other hand, the EJSD -
nodel-simulated sea level is 5 cm to 10 cm higher than the one simulated by NJSD model
n the South China Sea and Karimata Strait.
These HYCOM-estimated sea levels are validated using tide gauge sea levels. The
m-situ sea level data (1993-1999) recorded at Jakarta, Jepara (near Semarang) and
Surabaya have been obtained from the National Coordinating Agency for Surveys and
Mapping of Indonesia (Bakosurtanal). In addition the tide gauge at Singapore that derived
from University of Hawaii Sea Level Center (UHSLC) is also used to validate the simulated
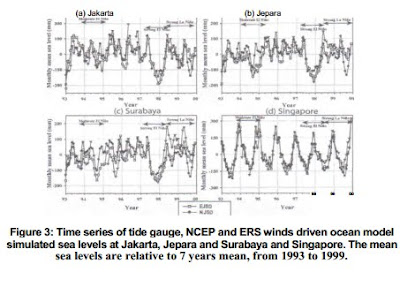
mean sea levels at the Karimata Strait. Figures 3, 4 and 5 show the validation results of
simulated monthly mean sea levels. The tide gauge and HYCOM show that sea levels are
low during the El Nino periods (Figure 3). The results of validation for the BSD model
show that correlation coefficients (CC) are ranging from 0.72 to 0.89 and the root mean
square errors (RMSE) are varying from 40 mm to 61 mm (Figure 4). On the other hand,
the NJSD model-simulated mean sea level has the CC from 0.53 to 0.85 and RMSE from 47
mm to 76 mm (Figure 5). These results indicate that the accuracy of the FJSD model is
higher than NJSD model. However, only at Jakarta, the EJSD model-simulated mean sea
level has a lower CC and a higher RMSE than NJSD modelled mean sea level. This is
probably caused by the lower ERS wind speed and stress than NCEP wind speed and
stress at the northern Jakarta (refer to Figures 6 and 7).
On the other hand, according to Sofian et al. [11], the absolute dynamic topography
(ADT) derived from various altimeters [12] shows the RMSE from 40 mm to 60 mm
against the tide gauge mean sea level. This fact indicates that the accuracies of the two
models are comparable with the one derived from ADT.
The signal of ENSO can be seen in both of the model and the tide gauge data at the
Java Sea. The tide gauge and simulated sea levels abruptly increase during the transition
period from strong El Nino (1997/1998) to strong La Nina (1998/1999), though the
simulated sea levels at Jepara and Surabaya tend to be lower than tide gauge sea levels
during this period as shown in Figure 3. On the other hand, the signal of ENSO is not
clearly seen in both of the model and tide gauge at Singapore. Eventually, the EJSD model
shows a better agreement with observation than the NJSD model, in terms of higher CC
and smaller RMSE. The summary of validation results between the simulated and tide
gauge mean sea levels is depicted in Table 2.
Wind Climatology
In this section, wind vector patterns in the Indonesian Sea are compared between
ERS and NCEP wind fields. The climate of the Indonesian Sea is characterized by
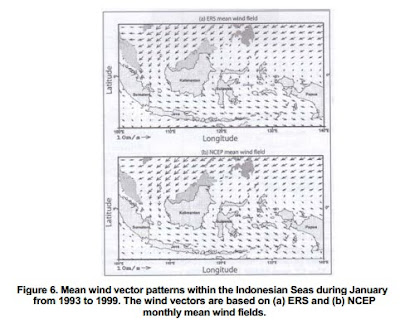
monsoonal winds and high rainfall. Figures 6 and 7 shows the wind vector patterns within
ne Indonesian Seas during January and August from 1993 to 1999. The mean wind vector
patterns are calculated based on monthly mean ERS and NCEP wind fields. Winds blow
*rom the south, curving across the equator with a westward component in the south, and
an eastward component in the north, from May to September, the wind direction is nearly
opposite during November to March [13]. During the southeast monsoon from May to
September, the easterly and southerly winds blow in the Java Sea and the Makassar Strait,
respectively. On the other hand, during the northwest monsoon from November to March,
wind direction over the Java Sea and Makassar Strait change to westerly and northerly,
respectively. In other words, the Java Sea is dominated by the zonal wind throughout the
year.
Figures 8 show the ERS and NCEP-derived Java Sea zonal winds (JZW) and wind
stresses (JZS). Assuming that the entire JZW and JZS are homogeneous, the JZW and
JZS are defined as the average zonal wind and wind stress from 105°E to 115°E and from
7.5°S to 2.5°S. The 7 years means of ERS and NCEP-derived JZW are -1.5 m/s and -0.6
s, respectively. Moreover, the 7 years means of ERS and NCEP-derived JZS are -0.015
N/m
2
and -0.003 N/m
2
, respectively. These indicate the JZS tends to be easterly.
The JZW and JZS follow the monsoon seasons. The strongest westerly JZW westerly
JZS) and easterly JZW (easterly JZS) occur during January and August, respectively. The
westerly ERS JZW is 1.0 m/s higher than the NCEP JZW in December to January. On the
other hand, the easterly ERS JZW is 2.5 m/s higher than the NCEP JZW, n August.
Similarly, the westerly and easterly ERS JZS are 0.01 N/m
2
and 0.03 N/m
2
higher than
NCEP JZS, in December to January and August, respectively. These differences n wind
speed and stress can lead to the different surface currents in the Java Sea and the
Makassar Strait, which will be discussed in the following sections.
Wind and Surface Current
Figures 9 and 10 show the surface currents based on the EJSD and NJSD models
in January (northwest monsoon) and August (southeast monsoon). Generally, the EJSD
model-simulated surface current speeds at the Java Sea are 5 cm/s to 10 cm/s faster than
NJSD model-simulated one both in January and August. During the northwest monsoon,
as the northwesterly wind blows, the monsoonal wind expels the Java Sea water to
eastward and the Karimata Strait water to the south. The Sunda Strait surface current is
eastward and enters from the Indian Ocean to the Java Sea during this period. Conversely,
the wind direction is changed to southeasterly during the southeast monsoon. The winddriven westward current drives the Java Sea and the Karimata Strait surface waters
westward and northward, respectively. The Sunda Strait surface water exits from the Java
Sea to the Indian Ocean during the southeast monsoon.
The Makassar Strait current does not follow the monsoonal wind direction. The
Makassar Strait surface currents tend to flow southward throughout the year. The
southward Makassar Strait surface current speed is low during the northwest monsoon
period, though the northerly wind is intensive. The low southward Makassar Strait surface
current speed seems to be inhibited by the strong Java Sea eastward current. On the other
hand, the southward Makassar Strait surface current speed is getting faster during the
southeast monsoon. It is known that, the strong southward Makassar Strait surface current
pushes the surface water with low salinity and low temperature back to the Java Sea [5].
Java Sea Volume Transport
In this section, the Java Sea volume transports are compared between the
EJSD and NJSD. The Java Sea volume transport is determined from the
meridional cross section from 7.0°S to 3.5°S at 114.0°E. The time series of the
Java Sea volume transports from January 1993 to December 1999 is depicted in
Figure 11. The positive volume transport ndicates the eastward volume transport.
In general, the Java Sea transport is directed eastward during the northwest
monsoon, and to the westward during the southeast monsoon, following the
monsoonal wind-induced surface current.
Figure 12 shows the climatology of the Java Sea volume transport. The
positive and negative volume transport indicates the eastward and westward
volume transports, respectively. Generally, the EJSD model-simulated volume
transport is larger than the one simulated by the NJSD model. The eastward and
westward EJSD model-simulated volume transports in August and December are
0.30 Sv (1 Sv = 1 million m
3
/s) and 0.23 Sv larger than the ones simulated by NJSD
model, respectively. The larger ERS than NCEP-derived wind stress (refer to
Figures) causes the larger EJSD than NJSD model-simulated volume transport in
August and December, respectively. The EJSD and NJSD model-simulated
volume transports have two peaks. The peak of the eastward EJSD and NJSD
model-simulated volume transports occur in December and January. The peak of
the westward EJSD volume transport occurs in August and reaches to -0.48 Sv,
while the NJSD model-simulated volume transport is about -0.20 Sv from June to
August.
CONCLUSIONS
The simulation of the Java Sea and Makassar Strait is conducted by using
HYCOM, which is driven by ERS and NCEP winds. The modelled mean sea levels
are validated with the tide gauge mean sea levels. The results of comparison
between the EJSD-simulated and tide gauge mean sea levels show that CC
ranges from 0.72 to 0.89, and RMSEs are from 40 mm to 61 mm. On the other
hand, the NJSD-simulated mean sea level has the CC from 0.53 to 0.84, and
RMSE from 47 mm to 76 mm. The EJSD model shows a better agreement with
observation than the NJSD model, in terms of higher CC and smaller RMSE. The
accuracy of the HYCOM modelled mean sea level is found to be comparable to that
of altimeter-derived ADT. The signal of ENSO can be seen in both of the model
and the tide gauge data within the Java Sea. The tide gauge and simulated sea
levels abruptly ncrease during the transition period from strong El Nino
(1997/1998) to strong La Nina 1998/1999), though the simulated sea levels at
Jepara and Surabaya tend to be lower than tide gauge sea levels during this
period.
Due to the shallowness of the Java Sea, the volume transport is dominated
by the wind. The westerly and easterly ERS wind stresses are 0.01 N/m
2
and 0.03
N/m
2
higher tnan NCEP wind stresses, in December and August, respectively.
Moreover, the ERS mean .vind speed is 1.0 m/s and 2.5 m/s higher than NCEP
mean wind speed, during the -orthwest and southeast monsoons, respectively.
The model results indicate that the Java Sea eastward volume transport simulated
by the EJSD model is larger than the one simulated by the NJSD model. The
EJSD model-simulated Java Sea eastward and
westward volume transports are 0.23 Sv and 0.30 Sv larger than the ones
simulated by the NJDS in December and August, respectively.
Acknowledgement
We thank HYCOM consortium to provide the HYCOM code. The ERS wind
data are provided by IFREMER. NCEP wind data are provided by NOAA CDC.